MongoDB® is database software that stores data in the same format as JSON. The data structure of the database can be changed when required. The performance of the database is good and developers can easily use to it to connect their code to the database.
The database, MongoDB is platform independent and runs in the same way on all platforms. It is an open source database and is based on a document-oriented database model. Various forms of data whether text, images, or videos can be stored in the database.
MongoDB and Why It’s So Popular?
Every record in the database is a document and has field and value pairs. The fields act as a column while the values depend on the data types. The primary key can be assigned to a field, which can connect other tables.
The Mongo shell can be used to write queries. After the installation of the software, mongo shell can be connected to the MongoDB.
Mongodb is the most popular NoSQL database, which helps the users to retrieve data easily. Users do not have to master SQL and users can use simple queries for writing and reading data. MongoDB is also the preferred choice for those who use JavaScript MEAN stack.
As we become familiar with the database and how it works and get to know its popularity and use, database administrators and tech professionals might choose any institution to acquire a MongoDB Certification which benefits you by widening your knowledge about the database and stand you out of the crowd.
Replication in MongoDB
The group of mongod processes creates replicas of a database in order to maintain the same set of data as in the original database. The replica of a database helps in easy deployments.
Now take a rundown where I have explained in detail about the MongoDB replication.
#Redundancy and Data Availability
Replication of a database helps in easy availability of data. The multiple copies of a database in the form of replicas avoids data loss as if a server crashes, data can be recovered from other servers for the same database.
Replication also provides easy data read as multiple users can send requests on the same database and get the data quickly. The distribution of data in such a way helps to easily create and deploy distributed applications.
#Replica
The replica set of a database is a group of mongod instances. Each replica set has many data bearing nodes along with optional arbiter nodes. There is only one node that can be used as a primary node while the rest of the nodes are secondary. The power of write operations is with the primary node only.
The changes done are maintained in an oplog through which all the secondary nodes are replicated. There are some circumstances in which another node can be used as a primary node but it happens very rarely.
In this diagram, write and read operations are done on the primary node and the secondary nodes are being updated.
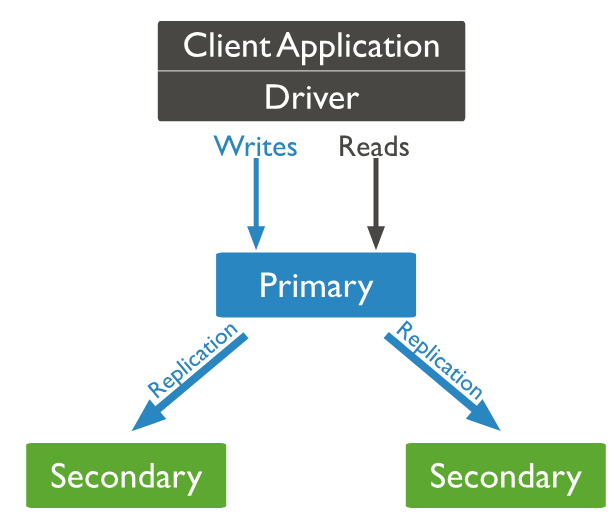
If the primary node is unavailable due to some reason, an eligible secondary node acts as a primary node to provide the data.
#Arbiter
Arbiter can also be added as a mongod instance. Though an arbiter does not perform the maintenance of dataset, it maintains a quorum and responds to other secondary nodes by responding to the heartbeat and nomination request by other replica sets. In this diagram, the arbiter is shown.
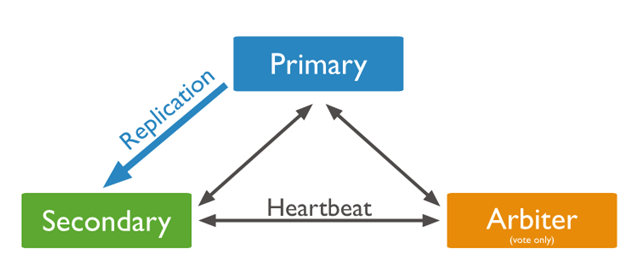
#Asynchronous Replication
Secondary nodes update themselves from the primary node asynchronously. This is useful because the failure of one or more nodes does not affect the functioning of the database and users can easily retrieve data.
#Automatic Failover
There are situations when the primary node is unable to communicate with other nodes. In this case, a secondary node makes itself as a primary node and the database functions normally. The secondary nominates itself as primary only if the communication electiontimeoutMiliis period extends beyond ten seconds.
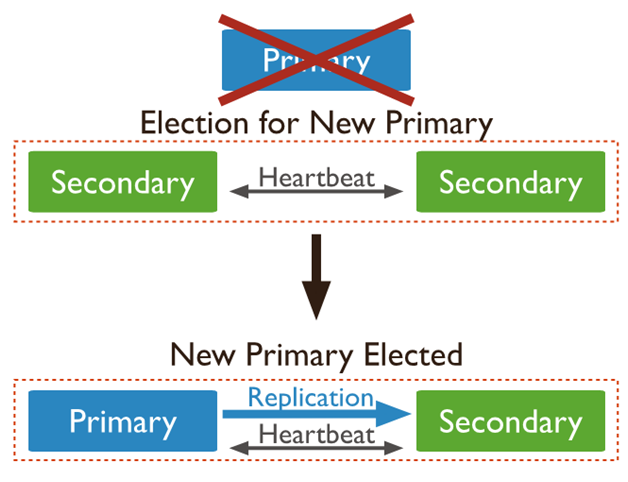
The write queries do not process until a secondary node has been nominated as a primary node but read queries work normally. The nomination of a secondary node as the primary node should not exceed 12 seconds as per the replica configuration settings. This time can be modified by using settings.electionTimeoutMillis.
The replica configuration settings include the following settings in order to set secondary as primary.
settings.chainingAllowed
It has three options
- Optional
- Type: boolean
- Default: true
The secondary nodes can replicate from other members if the default is set to true. If it is false then the secondary node can update itself only from the primary only.
settings.getLastErrorModes
- Optional
- Type: document
The document in the type variable decides whether the data has been successfully written.
settings.heartbeatTimeoutSecs
- Optional
- Type: int
- Default: 10
This sets the number of seconds for a replica set to wait for a successful heartbeat from each other. If the response time of a member do not succeed, then other members that unresponsive member as inaccessible.
settings.electionTimeoutMillis
- Optional.
- Type: int
- Default: 10000 (10 seconds)
The default time is set in milliseconds to check whether the primary node is accessible or not.
settings.catchUpTimeoutMillis
- Optional.
- Type: int
- Default: -1
The time is set in milliseconds for the new primary node and its sync with other replicas. High time reduces the amount of data to be rolled back by other members but increases failover time.
settings.catchUpTakeoverDelayMillis
- Optional.
- Type: int
- Default: 30000 (30 seconds)
If a node determines that it is ahead of the primary node then it declares itself as a primary node.
#Read Operations
Users can read from primary node only but if they specify a read preference through secondary nodes, they will be able to retrieve data through that source also.
Final Verdict
It can be said that replicating a MongoDB database is very easy and it helps in building distributed applications. The database replica can be deployed on many servers.
So if a server fails, data can be retrieved from other servers and this will not damage the functioning of the database. JavaScript Professionals can also use this database very easily as they do not have to master SQL and can get data through simple queries.
All images are from the MongoDB Manual on replication
— The content in this blog is provided in good faith by members of the open source community. The content is not edited or tested by Percona, and views expressed are the authors’ own. When using the advice from this or any other online resource, please test ideas before applying them to your production systems, and **always **secure a working back up.
Leaf image Photo by Chris Lawton on Unsplash ∎




Discussion
We invite you to our forum for discussion. You are welcome to use the widget below.