The goal of this tutorial is to show you how to use multi-master to aggregate databases with the same name, but different data from different masters, on the same slave.
Example:
- master1 => a French subsidiary
- master2 => a British subsidiary
Both have the same database PRODUCTION but the data are totally different.
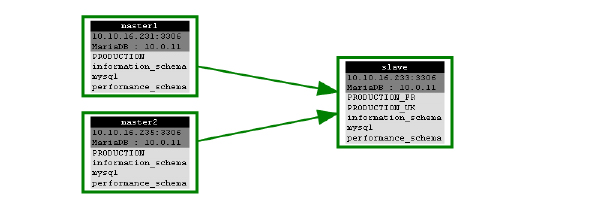
We will start with three servers—2 masters and 1 slave—you can add more masters if needed. For this tutorial, I used Ubuntu 12.04. I’ll let you choose the right procedure for your distribution fromDownloads.
Scenario
- 10.10.16.231 : first master (referred to subsequently as master1) => a French subsidiary
- 10.10.16.232 : second master (referred to subsequently as master2) => a British subsidiary
- 10.10.16.233 : slave (multi-master) (referred to subsequently as slave)
If you already have your three servers correctly installed, you can scroll down directly to “Dump your master1 and master2 databases from slave”.
Default installation on 3 servers
apt-get -y install python-software-properties
apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xcbcb082a1bb943db
```The main reason I put it in a different file because we use [Chef](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chef_(software)) as the configuration manager and this overwrites /etc/apt/sources.list . The other reason is that if any trouble occurs, you can just remove this file and restart with the default configuration.```
echo "deb http://mirror.stshosting.co.uk/mariadb/repo/10.0/ubuntu precise main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mariadb.list
apt-get update
apt-get install mariadb-server
The goal of this small script is to get the IP of the server and make a CRC32 from this IP to generate one unique server-id. Generally the command CRC32 isn’t installed, so we will use the one from MySQL. To set account // password we use the account system of Debian / Ubuntu.
Even if your server has more interfaces, you should have no trouble because the IP address should be unique.
user=`egrep user /etc/mysql/debian.cnf | tr -d ' ' | cut -d '=' -f 2 | head -n1 | tr -d 'n'`
passwd=`egrep password /etc/mysql/debian.cnf | tr -d ' ' | cut -d '=' -f 2 | head -n1 | tr -d 'n'`
ip=`ifconfig eth0 | grep "inet addr" | awk -F: '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}' | head -n1 | tr -d 'n'`
crc32=`mysql -u $user -p$passwd -e "SELECT CRC32('$ip')"`
id_server=`echo -n $crc32 | cut -d ' ' -f 2 | tr -d 'n'`
This configuration file is not one I use in production, but a minimal version that’s shown just as an example. The config may work fine for me, but perhaps it won’t be the same for you, and it might just crash your MySQL server.
If you’re interested in my default installof MariaDB 10 you can see it here: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Esysteme/Debian/master/mariadb.sh (this script as been updated since 4 years)
example:
./mariadb.sh -p 'secret_password' -v 10.3 -d /src/mysql
cat >> /etc/mysql/conf.d/mariadb10.cnf << EOF
[client]
# default-character-set = utf8
[mysqld]
character-set-client-handshake = FALSE
character-set-server = utf8
collation-server = utf8_general_ci
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
external-locking = off
skip-name-resolve
#make a crc32 of ip server
server-id=$id_server
#to prevent auto start of thread slave
skip-slave-start
[mysql]
default-character-set = utf8
EOF
We restart the server
/etc/init.d/mysql restart
* Stopping MariaDB database server mysqld [ OK ]
* Starting MariaDB database server mysqld [ OK ]
* Checking for corrupt, not cleanly closed and upgrade needing tables.
Repeat these actions on all three servers.
Create users on both masters
Create the replication user on both masters
on master1 (10.10.16.231)
mysql -u root -p -e "GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'replication'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'passwd';"
on master2 (10.10.16.232)
mysql -u root -p -e "GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'replication'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'passwd';"
Create a user for external backup
On master1 and on master2
mysql -u root -p -e "GRANT SELECT, LOCK TABLES, RELOAD, REPLICATION CLIENT, SUPER ON *.* TO 'backup'@'10.10.16.%' IDENTIFIED BY 'passwd' WITH GRANT OPTION;"
If you are just testing…
If you don’t have a such a configuration and you want to set up tests:
Create a database on master1 (10.10.16.231)
master1 [(NONE)]> CREATE DATABASE PRODUCTION;
Create a database on master2 (10.10.16.232)
master2 [(NONE)]> CREATE DATABASE PRODUCTION;
Dump your master1 and master2 databases from slave (10.10.16.233)
All the commands from now until the end have to be carried out on the slave server
- –master-data=2 get the file (binary log) and its position, and add it to the beginning of the dump as a comment
- –single-transaction This option issues a BEGIN SQL statement before dumping data from the server (this works only on tables with the InnoDB storage engine)
mysqldump -h 10.10.16.231 -u root -p --master-data=2 --single-transaction PRODUCTION > PRODUCTION_10.10.16.231.sql
mysqldump -h 10.10.16.232 -u root -p --master-data=2 --single-transaction PRODUCTION > PRODUCTION_10.10.16.232.sql
Create both new databases:
slave[(NONE)]> CREATE DATABASE PRODUCTION_FR;
slave[(NONE)]> CREATE DATABASE PRODUCTION_UK;
Load the data:
mysql -h 10.10.16.233 -u root -p PRODUCTION_FR < PRODUCTION_10.10.16.231.sql
mysql -h 10.10.16.233 -u root -p PRODUCTION_UK < PRODUCTION_10.10.16.232.sql
Set up both replications on the slave
Edit both dumps to get file name and position of the binlog, and replace it here: (use the command “less” instead of other commands in huge files)
French subsidiary – master1
less PRODUCTION_10.10.16.231.sql
get the line : (the MASTER_LOG_FILE and MASTER_LOG_POS values will be different to this example)
-- CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000010', MASTER_LOG_POS=771;
replace the file and position in this command:
CHANGE MASTER 'PRODUCTION_FR' TO MASTER_HOST = "10.10.16.231", MASTER_USER = "replication", MASTER_PASSWORD ="passwd", MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000010', MASTER_LOG_POS=771;
English subsidiary – master2
less PRODUCTION_10.10.16.232.sql
get the line: (the MASTER_LOG_FILE and MASTER_LOG_POS values will be different to this example, and would normally be different between master1 and master2. It’s just in my test example they were the same)
-- CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000010', MASTER_LOG_POS=771;
replace the file and position in this command:
CHANGE MASTER 'PRODUCTION_UK' TO MASTER_HOST = "10.10.16.232", MASTER_USER = "replication", MASTER_PASSWORD ="passwd", MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000010', MASTER_LOG_POS=771;
Rules of replication on config file
Unfortunately, the option replicate-rewrite-db doesn’t exist for variables, and we cannot set up this kind of configuration without restarting the slave server. In the section relating to the slave, add the following lines to
/etc/mysql/my.cnf
add these lines :
PRODUCTION_FR.replicate-rewrite-db="PRODUCTION->PRODUCTION_FR"
PRODUCTION_UK.replicate-rewrite-db="PRODUCTION->PRODUCTION_UK"
PRODUCTION_FR.replicate-do-db="PRODUCTION_FR"
PRODUCTION_UK.replicate-do-db="PRODUCTION_UK"
After that, you can restart the daemon without a problem – but don’t forgot to launch the slaves because we skipped that at the start ;).
/etc/init.d/mysql restart
Start the replication:
- one by one
START SLAVE 'PRODUCTION_FR';
START SLAVE 'PRODUCTION_UK';
- all at the same time:
START ALL SLAVES;
Now to check the replication:
slave[(NONE)]>SHOW SLAVE 'PRODUCTION_UK' STATUS;
slave[(NONE)]>SHOW SLAVE 'PRODUCTION_FR' STATUS;
slave[(NONE)]>SHOW ALL SLAVES STATUS;
Tests
on slave:
slave [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION_FR;
DATABASE changed
slave [PRODUCTION_FR]> SHOW TABLES;
Empty SET (0.00 sec)
slave [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION_UK;
DATABASE changed
slave [PRODUCTION_UK]> SHOW TABLES;
Empty SET (0.00 sec)
on master1:
master1 [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION;
DATABASE changed
master1 [PRODUCTION]>CREATE TABLE `france` (id INT);
Query OK, 0 ROWS affected (0.13 sec)
master1 [PRODUCTION]> INSERT INTO `france` SET id=1;
Query OK, 1 ROW affected (0.00 sec)
on master2:
master2 [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION;
DATABASE changed
master2 [PRODUCTION]>CREATE TABLE `british` (id INT);
Query OK, 0 ROWS affected (0.13 sec)
master2 [PRODUCTION]> INSERT INTO `british` SET id=2;
Query OK, 1 ROW affected (0.00 sec)
on slave:
-- for FRANCE
slave [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION_FR;
DATABASE changed
slave [PRODUCTION_FR]> SHOW TABLES;
+-------------------------+
| Tables_in_PRODUCTION_FR |
+-------------------------+
| france |
+-------------------------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
slave [PRODUCTION_FR]> SELECT * FROM france;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
-- for British
slave [(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION_UK;
DATABASE changed
slave [PRODUCTION_UK]> SHOW TABLES;
+-------------------------+
| Tables_in_PRODUCTION_UK |
+-------------------------+
| british |
+-------------------------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
slave [PRODUCTION_UK]> SELECT * FROM british;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 2 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
It works!
If you want do this online, please add +1 to: https://jira.mariadb.org/browse/MDEV-17165
Limitations
WARNING: it doesn’t work with the database specified in query. (With Binlog_format = STATEMENT or MIXED)
This works fine:
USE PRODUCTION;
UPDATE `ma_table` SET id=1 WHERE id =2;
This query will break the replication:
USE PRODUCTION;
UPDATE `PRODUCTION`.`ma_table` SET id=1 WHERE id =2;
=> databases PRODUCTION does not exist on this server.
A real example
Missing update
on master1:
master1 [(NONE)]>UPDATE `PRODUCTION`.`france` SET id=3 WHERE id =1;
Query OK, 1 ROW affected (0.02 sec)
ROWS matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
master1 [(NONE)]> SELECT * FROM `PRODUCTION`.`france`;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 3 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
on slave:
slave [PRODUCTION_FR]> SELECT * FROM france;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
In this case we missed the update. It’s a real problem, because if the replication should crash, our slave is desynchronized with master1 and we didn’t realize it.
Crash replication
on master1:
master1[(NONE)]> USE PRODUCTION;
DATABASE changed
master1 [PRODUCTION]> SELECT * FROM`PRODUCTION`.`france`;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 3 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
master1 [PRODUCTION]>UPDATE `PRODUCTION`.`france` SET id=4 WHERE id =3;
Query OK, 1 ROW affected (0.01 sec)
ROWS matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
master1 [PRODUCTION]> SELECT * FROM `PRODUCTION`.`france`;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 4 |
+------+
1 ROW IN SET (0.01 sec)
on PmaControl: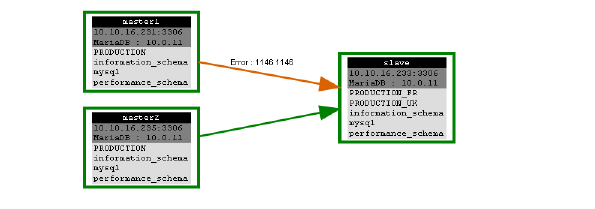
slave [PRODUCTION_FR]> SHOW slave 'PRODUCTION_FR' STATUSG;
*************************** 1. ROW ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting FOR master TO send event
Master_Host: 10.10.16.231
Master_User: replication
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000010
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 2737
Relay_Log_File: mysqld-relay-bin-production_fr.000003
Relay_Log_Pos: 2320
Relay_Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000010
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: No
Replicate_Do_DB: PRODUCTION_FR
Replicate_Ignore_DB:
Replicate_Do_Table:
Replicate_Ignore_Table:
Replicate_Wild_Do_Table:
Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table:
Last_Errno: 1146
Last_Error: Error 'Table 'PRODUCTION.france' doesn't exist' on query. Default database: 'PRODUCTION_FR'. Query: 'UPDATE `PRODUCTION`.`france` SET id=4 WHERE id =3'
Skip_Counter: 0
Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 2554
Relay_Log_Space: 2815
Until_Condition: None
Until_Log_File:
Until_Log_Pos: 0
Master_SSL_Allowed: No
Master_SSL_CA_File:
Master_SSL_CA_Path:
Master_SSL_Cert:
Master_SSL_Cipher:
Master_SSL_Key:
Seconds_Behind_Master: NULL
Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No
Last_IO_Errno: 0
Last_IO_Error:
Last_SQL_Errno: 1146
Last_SQL_Error: Error 'TABLE 'PRODUCTION.france' doesn't exist' ON query. DEFAULT DATABASE: 'PRODUCTION_FR'. Query: 'UPDATE `PRODUCTION`.`france` SET id=4 WHERE id =3'
Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids:
Master_Server_Id: 2370966657
Master_SSL_Crl:
Master_SSL_Crlpath:
Using_Gtid: No
Gtid_IO_Pos:
1 ROW IN SET (0.00 sec)
ERROR: No query specified
And we got the error which crash replication : Error TABLE ‘PRODUCTION.france’ doesn’t exist’ ON query. DEFAULT DATABASE: ‘PRODUCTION_FR’. Query: ‘UPDATE PRODUCTION.france SET id=4 WHERE id =3
NB : Everything works fine with binlog_format=ROW.
Author: Aurélien LEQUOY <aurelien.lequoy@esysteme.com> you don’t copy/paste the email, it won’t work. You didn’t think I would post it like that in the open for all bots, right? ;).
License
This article is published under: The GNU General Public License v3.0 http://opensource.org/licenses/GPL-3.0
Others
The point of interest is to describe a real use case with full technical information to allow you to reproduce it by yourself. This article was originally published just after the release of MariaDB 10.0 on the now defunct website www.mysqlplus.net. ∎




Discussion
We invite you to our forum for discussion. You are welcome to use the widget below.